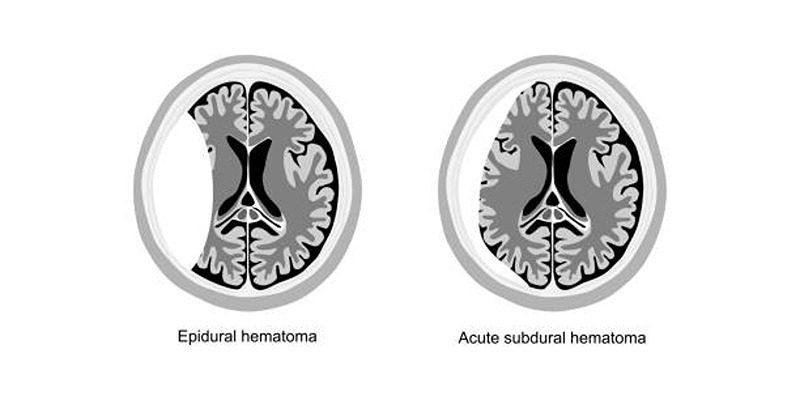
Epidural Hematoma: Causes and Associated Risks Explained
Advertisement
The medical condition called epidural hematoma shows itself through excessive blood pooling between brain tissue and its covering dura mater in addition to the skull interior. The harmful effect of a traumatic head injury causes this medical condition which rapidly builds up brain pressure requiring immediate medical attention. The primary causes of epidural hematomas occur through strong traumatic incidents including automobile accidents and falls and sports-related accidents. Such a condition presents symptoms through severe headache while causing nausea and confusion and leading to unconsciousness.
What Is an Epidural Hematoma?
An epidural hematoma is a serious medical condition where blood collects between the skull and the brain's outer protective layer, known as the dura mater. It typically results from severe head trauma—such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury—that ruptures blood vessels in this area. The pooling blood creates pressure on the brain, leading to symptoms like intense headaches, dizziness, confusion, nausea, or even loss of consciousness.
Without swift medical attention, this pressure can cause severe, life-threatening complications. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical, with emergency care often involving surgery to remove the blood and alleviate pressure on the brain.
Symptoms of Epidural Hematoma:
Epidural hematoma symptoms may appear immediately after an injury or gradually develop over several hours. Common signs to watch for include:
- Intense headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- A brief loss of consciousness followed by a temporary period of alertness (known as a lucid interval)
- Confusion or disorientation
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Enlarged pupils, typically on the side of the head injury
- Seizures
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech
Causes of Epidural Hematoma:
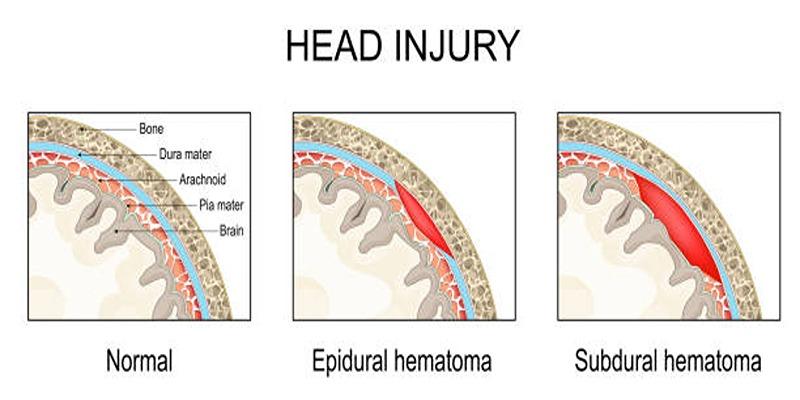
Epidural hematomas are most commonly caused by head injuries that result in arterial bleeding, often from the middle meningeal artery. Below are the primary causes:
1. Traumatic Head Injuries
A direct blow to the head—whether from a fall, a sports collision, or a car accident—is the leading cause of epidural hematomas. Such impacts can fracture the skull and rupture arteries like the middle meningeal artery, leading to rapid blood accumulation between the skull and the dura mater.
2. Blunt Force Trauma
Blows to the head from falling objects, physical altercations, or accidental strikes can also cause epidural hematomas. These injuries are particularly dangerous when they occur in the temporal or parietal regions of the skull, where the bones are thinner and more prone to fractures.
3. Falls
Falls are a significant cause of epidural hematomas, especially among older adults and young children. Older adults often face a higher risk due to balance issues and weakened bone density, while children are more vulnerable due to their active play and lack of hazard awareness.
4. Sports-Related Injuries
Contact sports such as football, boxing, rugby, and hockey pose a high risk for head injuries and epidural hematomas. Players in these sports are frequently exposed to high-impact collisions or blows to the head, which may not always show immediate symptoms.
5. Workplace Accidents
Occupational hazards, particularly in high-risk jobs such as construction, manufacturing, or warehouse work, are another major cause of epidural hematomas. Falls from heights, being struck by heavy objects, or accidents involving machinery can result in severe head trauma.
Preventing Epidural Hematoma:
While not all head injuries are avoidable, certain precautions can significantly reduce the risk of an epidural hematoma:
- Wear Helmets – A necessity for motorcyclists, cyclists, and athletes in contact sports to protect against severe head injuries.
- Use Seatbelts – Crucial for minimizing head trauma during vehicle accidents.
- Prevent Falls – Install handrails, use non-slip flooring, and ensure proper lighting to reduce fall risks, particularly for older adults.
- Prioritize Workplace Safety – Adhere to safety protocols and wear protective gear in hazardous environments.
Risks Associated with Epidural Hematoma:
An untreated epidural hematoma can result in serious and potentially life-threatening complications. Key risks include:
1. Increased Intracranial Pressure
As blood collects within the skull, it creates pressure on the brain, leading to swelling and the risk of significant brain damage.
2. Brain Herniation
Excessive pressure can force brain structures to shift out of position, compressing vital areas that control essential functions like breathing and heart activity.
3. Permanent Neurological Impairment
Even with timely treatment, an epidural hematoma may cause long-term effects such as memory loss, speech difficulties, or muscle weakness, depending on the injury's severity.
4. Seizures
Pressure and bleeding in the brain can provoke seizures, which may develop into a chronic condition requiring ongoing medical care.
5. Coma and Death
Without immediate medical intervention, an epidural hematoma can lead to unconsciousness, coma, and, in severe cases, fatal outcomes.
Diagnosing Epidural Hematoma:
Accurate diagnosis of an epidural hematoma relies on advanced imaging techniques and clinical evaluations. Key methods include:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan – The most commonly used and highly effective tool for identifying blood accumulation in the brain.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – Delivers detailed brain imaging but is less commonly used in emergency situations due to time constraints.
- Neurological Examination – Involves assessing motor skills, reflexes, and eye movements to determine brain function and detect abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Epidural Hematoma:
The treatment for an epidural hematoma depends on its size and severity. Common approaches include:
1. Emergency Surgical Intervention
For large or rapidly expanding hematomas, immediate surgery is often necessary to alleviate pressure on the brain. Surgical options include:
- Craniotomy – A portion of the skull is temporarily removed to access and remove the hematoma while controlling the source of bleeding.
- Burr Hole Drainage – A minimally invasive technique where small holes are drilled into the skull to drain accumulated blood.
2. Medications for Managing Symptoms
Medications play a vital role in supporting recovery and mitigating complications:
- Diuretics – Reduce brain swelling by encouraging the removal of excess fluid.
- Anticonvulsants – Administered to prevent seizures in high-risk cases.
- Pain Relievers – Carefully prescribed to control headaches and discomfort under professional supervision.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
The recovery process depends on the severity of the hematoma and the effectiveness of treatment. Patients may benefit from:
- Physical Therapy – To restore strength, balance, and coordination.
- Speech Therapy – To address challenges with communication and speech caused by the injury.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation – To rebuild memory, focus, and problem-solving skills when brain damage is present.
Conclusion:
Epidural hematoma is a serious medical emergency requiring immediate diagnosis and treatment to avoid life-threatening complications. Awareness of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take preventive steps and seek timely medical care. After a head injury, monitoring symptoms closely and getting emergency attention can make all the difference in ensuring the best possible outcome.
On this page
What Is an Epidural Hematoma? Symptoms of Epidural Hematoma: Causes of Epidural Hematoma: 1. Traumatic Head Injuries 2. Blunt Force Trauma 3. Falls 4. Sports-Related Injuries 5. Workplace Accidents Preventing Epidural Hematoma: Risks Associated with Epidural Hematoma: 1. Increased Intracranial Pressure 2. Brain Herniation 3. Permanent Neurological Impairment 4. Seizures 5. Coma and Death Diagnosing Epidural Hematoma: Treatment Options for Epidural Hematoma: 1. Emergency Surgical Intervention 2. Medications for Managing Symptoms Recovery and Rehabilitation: Conclusion:Advertisement